Data warehousing systems consolidate information from operational data sources into a centralized repository, allowing for analysis and mining of the combined data. During the integration process, source data is often transformed through a series of operations ranging from simple algebraic operations or aggregations to complicated "data cleansing" methods.
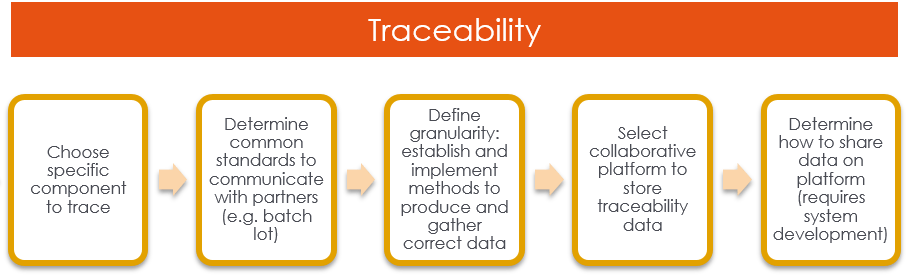
The capacity to ensure that your data is totally traceable throughout the entire landscape is referred to as data traceability. This allows you to swiftly track your data back to its original source.
To achieve clear and correct conclusions, you must be able to monitor any transformation, dead end, or relationship between data items. Data traceability is crucial when looking at source systems as well as reporting. It basically accounts for all data from the source to the current goal. Without data traceability, you can't be sure that all data is correct, which could influence future decisions. Data traceability also protects the accuracy of your information because you can view the data's whole journey from its inception to its current location.
It is occasionally important during data analysis to look not just at the information in the warehouse, but also at how that information was generated from the sources. Data lineage refers to the practice of tracing warehouse data objects back to the source data items from which they were produced. Tracing in a data warehouse environment provides various benefits and applications, including in-depth data analysis and mining, permission management, view updating, and the whole data lifecycle management wheel, including quick warehouse recovery.
Why Do We Want to Trace Data?
Data is at the heart of digital change. A corporation cannot support data that lacks integrity if it wishes to progress in its digital transformation projects. The integrity of any data is mostly determined by the trust that users have in it. And the majority of this confidence is founded on data traceability. It is impossible to determine if the results of the analysis are reliable in the absence of traceability.
Companies have been attempting to comprehend this idea for some time. You may be wondering why today's businesses require greater traceability. With a big volume of their data coming from unmanaged external sources (sensors, data streams, Internet of things), it is critical for businesses to monitor this data as it is generated.
We want unambiguous data traceability since the ultimate result of real-world data analysis differs significantly from the raw data input. This is because raw data input—for example, tables on tables of health records or claims data—must be cleaned, transformed, and linked before it can be analyzed. Decision-makers cannot be convinced that the approved data are authentically reflected in the outcomes of any data analysis unless each transformation or connection is tracked.
Data traceability increases the confidence of reviewers and decision-makers in real-world evidence studies. A unified, uniform approach to data traceability is a critical part of using real-world data in decision making. It is used to identify how the latter came from the former as well as when and in what order.
Benefits of Data Traceability
In a variety of businesses, traceability is useful before, during, and after development. It keeps track of what has been done so that you don't have to start over on a fresh build, for example. It makes it easy to estimate risk and avoid errors throughout development. It also makes demonstrating compliance faster and easier.
Governance
Ensure the traceability of upstream data to give quality and access controlled findings to owners and data sources. In addition to downstream traceability, data owners will be able to govern their procedure.This way they can prove compliance with regulations and industry best practices, building goodwill in the industry, and among customers and investors.
Data Quality
Ensuring the traceability of their data allows a company to ensure their data meets the required standards set within the company or industry practices. This guarantees the quality of the data being used and the authenticity of any decisions made based on it.
Risk Mitigation
When companies put effort into tracing data back to its source and keeping an eye on the process, they are able to find any security gaps that may compromise the data. This allows them to eliminate such risks before they are used by malicious targets or discovered by users, eroding their trust in the data quality.
Storage Optimization
Data traceability provides companies with a summary of the data being accessed as an input archiving choices and provisions. It identifies where, how frequently, and by whom access is authorized.
Conclusion
The influence that a change in a contact's position, service, residence, or even employer can have on a company's marketing, business, or maintenance service is not insignificant.
If a company produces something that needs them to keep track of specs, modifications, requests, outcomes, and versions, traceability is certainly a key element of their work. However, given how many businesses still maintain requirements manually and how many development teams rely on separate platforms for application data lifecycle management, the benefits of traceability are woefully underappreciated. Traceability is the key to taking data analysis to the next level.